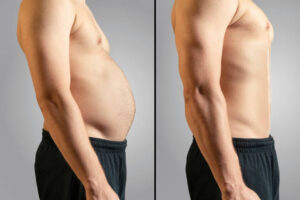
When it comes to burning fat, two popular cardio workouts dominate the fitness world: HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) and Steady-State Cardio. But which one helps you lose fat faster? In this article, we will compare these two workout styles to help you decide which one suits your goals best.
What is HIIT?
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a workout style that involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief rest periods. A typical HIIT session lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
Benefits of HIIT:
Burns More Calories in Less Time – HIIT workouts increase heart rate quickly, leading to more calorie burn.
Boosts Metabolism – The afterburn effect (EPOC) helps you burn calories even after the workout.
Preserves Muscle Mass – HIIT is effective for fat loss while maintaining lean muscle.
Improves Cardiovascular Health – It strengthens the heart and improves endurance.
No Equipment Needed – HIIT exercises like jumping jacks, burpees, and squats can be done anywhere.
What is Steady-State Cardio?
Steady-state cardio involves maintaining a moderate-intensity workout for a longer duration, typically 30 to 60 minutes. Examples include jogging, cycling, and swimming at a steady pace.
Benefits of Steady-State Cardio:
Good for Beginners – It is easy to perform and requires minimal experience.
Less Stress on Joints – A steady pace reduces injury risk compared to high-impact HIIT.
Burns Calories Efficiently – A longer workout session leads to consistent fat-burning.
Enhances Endurance – Improves stamina for long-duration physical activities.
Great for Mental Health – It helps reduce stress and improve mood.
HIIT vs. Steady-State Cardio: Which Burns Fat Faster?
1. Calorie Burn
HIIT burns more calories per minute due to its intensity.
Steady-state cardio burns fewer calories per minute but is performed for a longer duration.
Studies show that a 20-minute HIIT session can burn the same calories as a 40-minute steady-state workout.
2. Fat Loss
HIIT promotes fat oxidation (fat burning) due to its high intensity.
Steady-state cardio burns fat primarily during the workout, but HIIT triggers post-workout fat burning for up to 24 hours.
Research suggests HIIT is more effective for reducing belly fat than steady-state cardio.
3. Metabolism Boost
HIIT increases EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption), meaning you burn calories even after the workout ends.
Steady-state cardio has little post-workout calorie burn.
If you want continuous fat burning, HIIT is the better option.
4. Muscle Preservation
HIIT helps retain lean muscle while burning fat.
Steady-state cardio may lead to muscle loss if done excessively without strength training.
For a toned and fit look, HIIT is the preferred choice.
5. Sustainability & Enjoyment
HIIT can be intense and tough for beginners.
Steady-state cardio is easier to sustain long-term.
The best workout is the one you enjoy and can stick with consistently.
Who Should Choose HIIT?
If you have limited time and want quick results.
If you prefer short, intense workouts.
If you want to preserve muscle while losing fat.
Who Should Choose Steady-State Cardio?
If you enjoy longer, moderate workouts.
If you are a beginner or recovering from injury.
If you want a low-impact fat-burning method.
Combining HIIT and Steady-State for Maximum Fat Loss
For the best fat-burning results, you can combine both workouts:
3 Days of HIIT + 2 Days of Steady-State Cardio – This balances intensity and endurance.
HIIT on Busy Days, Steady-State on Rest Days – Helps with active recovery.
Strength Training + HIIT or Steady-State – Enhances fat loss while preserving muscle.
Conclusion: Which Burns Fat Faster?
HIIT burns fat faster due to its high-intensity, calorie-burning, and metabolism-boosting effects. However, steady-state cardio is great for long-term consistency and endurance. The best choice depends on your fitness level, goals, and personal preference.
To achieve the best fat loss results, consider mixing both HIIT and steady-state cardio into your fitness routine. Stay consistent, eat a balanced diet, and enjoy your workouts for sustainable fat loss!